Orinj version 9.0.0
The Orinj High Pass Filter removes the frequencies below some frequency (the cutoff frequency) and passes the frequencies above the cutoff frequency unchanged. See High pass filter for more information on this type of effect.
This is a high pass filter with a nonlinear phase response.
An example of the Orinj High Pass Filter
The following example contains two repetitions of an electric guitar riff. The first repetition is as recorded, without the high pass filter. The second one uses a high pass filter of order 6 at 400 Hz.
Click to play this example with a high pass filter.
Using the Orinj High Pass Filter
The Orinj High Pass Filter can be added to tracks, auxiliary channels, and the master channel in the session view and to waves in the single wave view.
- To add the effect to a track or an auxiliary channel in the session, first click on the track or auxiliary channel to select it. Click on Effect, Filtering, and then on Orinj High Pass Filter in the menu.
- To add the effect to the master channel in the session, click on Track and then on Master Channel in the menu. In the master channel dialog, click on the Add button.
- To add the effect to a wave in the single wave view, click on Effect, Filtering, and then on Orinj High Pass Filter in the menu.
You will see the following dialog.
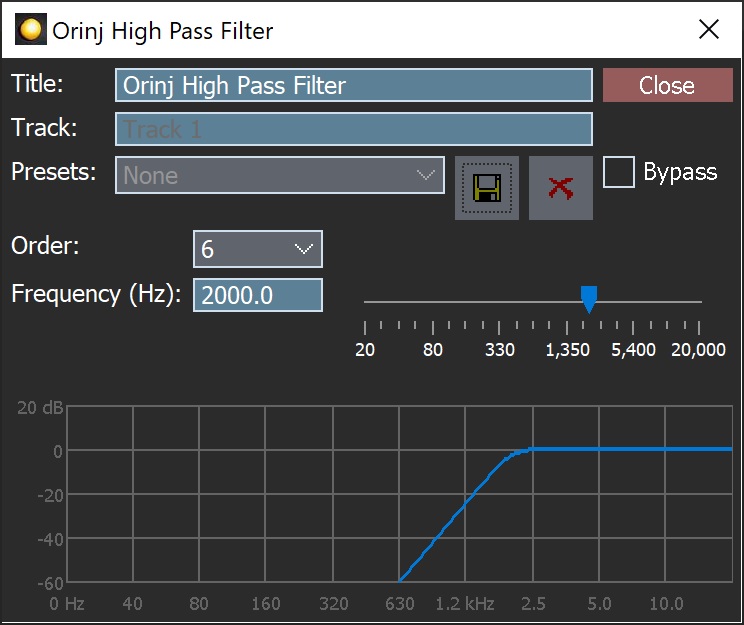
When this dialog becomes visible, the Orinj High Pass Filter effect has been added. Adjust the parameters of the high pass filter in the dialog above and click Close. The parameters are described below.
Orinj High Pass Filter parameters
See Orinj Effects for an explanation of the Title, Track, Presets, and Bypass controls. The remaining Orinj High Pass Filter controls are described below:
- Order: Use this drop-down box to set the order of the filter. This is a Butterworth high pass filter. At larger orders, the filter becomes more precise and its magnitude response transitions faster from the band in which frequencies are stopped to the band in which frequencies are preserved (the slope in the graph will become steeper and the transition frequency band narrower).
- Frequency: Use these controls – the box and the slider – to set the cutoff frequency of the filter. The cutoff frequency is the frequency at which the high pass filter transitions from the stop band to the pass band. An ideal high pass filter will do so suddenly, whereas a practical high pass filter will do so gradually. The magnitude response at the cutoff frequency in this filter is -3 dB. The frequency is measured in Hz and can be between 20 Hz and 20 kHz.
- Filter graph: This graph shows the actual equalization that occurs in the filter.
See Orinj Effects for additional notes on: where Orinj effects can be used, using boxes and sliders that impact the same parameter (such as the box and slider for the frequency), applying effects to mono and stereo waves, and using effects during playback. See Orinj Working with effects for additional information on creating, modifying, moving, and removing effects. See High pass filter for additional information on high pass filters in audio processing.
Automations
The Orinj High pass filter has one automation.
- Frequency: This automation adds or subtracts up to 20 kHz from the frequency.
Right-click on the corresponding controls to add or remove the automation.

Add new comment